Overview
As people age, maintaining a healthy weight becomes key to overall well-being. For seniors, the ideal BMI often ranges from 23 to 30, higher than standard adult charts. This guide explains how aging affects BMI, why muscle mass matters, and practical tips for nutrition, exercise, and long-term health.
As we age, maintaining a healthy weight becomes more important for overall well-being. Body Mass Index (BMI) is one of the most common tools used to assess whether a person is underweight, normal weight, overweight, or obese. But when it comes to older adults, interpreting BMI requires extra care. BMI for seniors may differ from younger adults because of changes in muscle mass, fat distribution, and metabolism. Understanding what ranges are considered healthy for older adults helps prevent health risks while supporting longevity and quality of life.
Understanding BMI
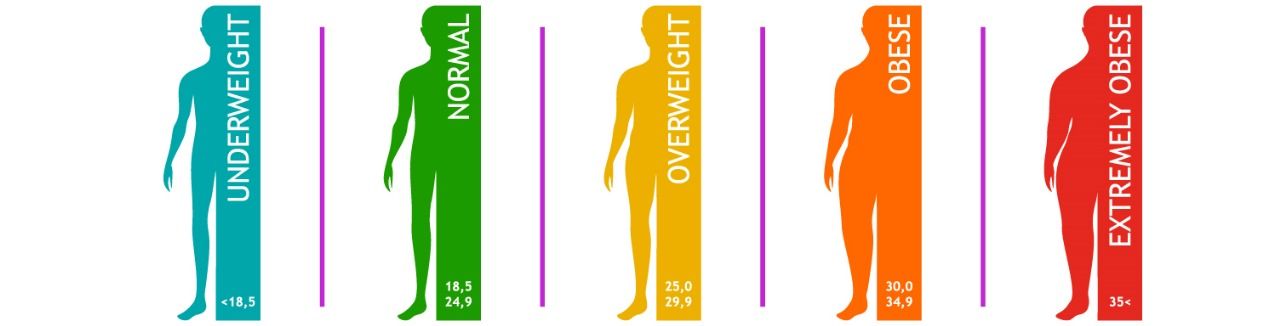
BMI is calculated by dividing weight in kilograms by height in meters squared. The standard categories are:
Underweight: below 18.5
Normal: 18.5 – 24.9
Overweight: 25 – 29.9
Obese: 30 and above
These categories were developed based on adults in general. However, the normal BMI for elderly populations may not align perfectly with these cutoffs, since body composition shifts with age.
💡 Tip: Instead of only depending on BMI, combine it with BMI calculators and other health checks for a more accurate picture.
BMI for Seniors: Why It’s Different
Aging brings a natural decline in muscle mass (sarcopenia) and a gradual increase in body fat, often around the abdomen. Two people can share the same BMI but have very different body compositions:
An older adult with BMI 23 may carry more body fat than a younger adult at the same BMI.
Being slightly above 25 may not carry the same risk in seniors as in younger adults, especially when muscle mass is preserved and metabolic markers look healthy.
Key factors that shift the picture:
Sarcopenia: less muscle lowers weight without improving health.
Visceral fat: abdominal fat can rise even if BMI stays stable.
Height changes: spinal compression and posture shifts can inflate BMI over time
💡 Tip: Seniors should not panic if slightly above “normal BMI” sometimes, a higher BMI offers protective benefits.
Healthy BMI for Older Adults
Research suggests that the healthy BMI for older adults is often higher than the standard adult range. While 18.5 to 24.9 is considered normal for younger adults, studies show that a BMI between 23 and 30 may be healthier for seniors.
Being slightly overweight might provide some protective benefits in older age, reducing the risks of frailty, bone fractures, and malnutrition. On the other hand, being underweight can increase the likelihood of health complications. Understanding what is a good BMI for seniors means looking at more than just the number—it’s about balancing weight with overall health.
💡 Tip: Focus on staying within this adjusted range rather than trying to match younger adult BMI charts.
Risks of Being Underweight or Overweight in Seniors
When BMI is too low
Weakened immunity and slower wound healing
Higher fall and fracture risk due to low muscle and bone density
Nutrient deficiencies and low energy
Greater frailty risk and reduced independence
When BMI is too high
Type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, and heart disease
Joint pain and limited mobility
Sleep apnea and lower quality of sleep
Reduced endurance and balance problems
💡 Tip: If BMI drops suddenly or rises sharply, consult a doctor for personalized advice.
Beyond BMI: Other Factors That Matter
BMI doesn’t reveal body composition or fat location. For seniors, add these to your toolkit:
Waist circumference: Aim for <102 cm (40 in) for men and <88 cm (35 in) for women, or lower if advised. Abdominal fat is a stronger risk signal than BMI alone.
Body fat %: Tools like bioelectrical impedance or DEXA scans estimate fat vs muscle.
Grip strength and leg strength: Easy proxies for functional fitness and fall risk.
Gait speed and balance: Helpful fall-prevention indicators.
Metabolic markers: Fasting glucose, A1C, lipids, blood pressure, and inflammation.
💡 Tip: Always pair BMI with body fat %, waist size, and strength tests for seniors.
Maintaining a Healthy BMI as You Age
Reaching and keeping a healthy BMI for older adults requires lifestyle habits tailored to aging bodies.
- Balanced Nutrition: Include protein-rich foods, calcium, and vitamins to support bone and muscle health.
- Physical Activity: Low-impact exercises like walking, swimming, or resistance training help maintain strength.
- Routine Monitoring: Regular checkups ensure any sudden weight loss or gain is addressed early.
These habits not only help maintain a healthy BMI but also improve energy and independence in later years.
💡Tip: Even simple daily walking helps maintain a healthy BMI. Use this guide How Much to Walk According to BMI
Practical Targets for Seniors
Use this as a guiding framework, not strict rules:
Underweight or BMI <22: prioritize calorie and protein intake, check for underlying issues.
BMI 23–27: maintain with balanced nutrition, steps, and strength training.
BMI 27–30: fine for many if waist and labs look good; focus on fitness and mobility.
BMI >30: consider gradual weight reduction through nutrition + resistance training, with clinical guidance.
Nutrition for a Healthy Senior BMI
Protein at every meal: Aim for 1.0–1.2 g/kg/day, or your clinician’s target. Include eggs, fish, poultry, Greek yogurt, tofu, lentils.
Colorful plants: Vegetables, fruits, beans, and whole grains for fiber and micronutrients.
Healthy fats: Olive oil, nuts, seeds, avocado for heart health and satiety.
Calcium and vitamin D: Support bone density; consider fortified foods as needed.
Hydration: Dehydration can reduce appetite and affect balance.
Smart snacks: Cottage cheese with berries, hummus with carrots, peanut butter on whole-grain toast.
Tip: If appetite is low, try smaller, more frequent meals, and protein smoothies.
Exercise: Preserve Muscle, Protect Mobility
Resistance training (2–3 days/week): Bands, light dumbbells, or body-weight moves maintain muscle and bone.
Walking or low-impact cardio (150 mins/week): Keeps heart health, mood, and blood sugar in check.
Balance work: Heel-to-toe walking, single-leg stands, or tai chi reduce fall risk.
Flexibility: Gentle stretching or yoga preserves range of motion.
Common Myths Busted
“Everyone should be 18.5–24.9.” Not for many seniors; 23–30 can be fine.
“BMI equals body fat.” It doesn’t. It’s an estimate based on height and weight.
“Weight loss is always good.” Not if it means muscle loss or frailty.
“Thin means healthy.” Low BMI with low strength is risky.
Sample One-Week Focus Plan
Goal: Support a stable BMI with better strength, energy, and waist health.
Daily anchors:
Protein 25–35 g at two meals; one 20–30 g snack
30–45 minutes of movement (mix walking and light strength)
Hydrate: 6–8 cups water, unless advised otherwise
Track: steps, simple strength moves, waist once a week
Weekly mix:
Mon: 25-minute walk + 10-minute band circuit
Tue: Balance drills + stretch; protein-rich lunch
Wed: 30-minute swim or brisk walk
Thu: Light dumbbells; chair squats and rows
Fri: 20-minute walk + core and posture work
Sat: Social activity—gardening, dancing, or a park stroll
Sun: Restorative stretch; plan protein for the week
Tip: Consistency beats intensity. Keep it doable.
Alternatives to BMI for Seniors
Since BMI has its limitations, other tools may provide better insight into health for seniors. Body fat percentage measurements, waist-to-hip ratio, and functional health assessments can all be valuable.
Still, BMI remains one of the simplest and most widely recognized ways to track weight-related health. When combined with other measures, it gives a more accurate picture of well-being in older adults.
💡 Tip: Use BMI as a quick check but rely on alternative tools for accuracy.
When to Seek Medical Advice
Sudden weight loss, unexplained weight gain, or difficulty maintaining a normal BMI for elderly should always be discussed with a doctor. These changes could signal underlying health problems that need attention. Personalized medical advice is especially important for seniors, as individual health factors vary greatly.
💡 Tip: Always discuss BMI results with your healthcare provider before making major changes.
Conclusion
So, what is a good BMI for seniors? While the standard ranges apply to most adults, research suggests that the average BMI for adults over 60 may fall slightly higher, often between 23 and 30. This range accounts for natural changes in muscle and fat as we age.
BMI remains a helpful guideline, but it shouldn’t be the only measure of health for seniors. Considering muscle mass, lifestyle, and overall wellness provides a clearer picture. By aiming for a healthy BMI for older adults, adopting balanced habits, and consulting with healthcare professionals, seniors can maintain strength, independence, and quality of life as they age.
👉 Use our free tool to here: Digital Calculator
